Nomenclature of organic compounds
Common names:
| Valeric acid | Pentanoic acid |
| Caproic acid | Hexanoic acid |
| Malic acid | HOOC-CH(OH)-CH2-COOH | Phosgene | Cl-CO-Cl |
| Urea/carbamide | NH2-CO-NH2 |
| Carbamic acid | NH2-COOH |
| Carbamoyl urea | NH2-CO-NH-CO-NH2 |
| Ethyl carbamate | NH2-CO-CH2-CH3 |
| Cyanamide | NH2-C≡N |
| Urethane | CH3-NH-CO-O-CH2-CH3 |
IUPACAuthority on chemical nomenclature and terminology prefixes and suffixes:
For aliphaticCompounds which do not have a ring or have a non aromatic ring and some aromaticCompounds that typically have 1 ring, the ring is continuously conjugated, has (4n+2)π electrons and is planar compounds:
| Group | prefix | suffix | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Halide | Halo- | _ | |
| Alcohol | Hydroxy- | -ol | |
| Carboxylic acid | Carboxy- | -oic acid | |
| Aldehyde | Formyl- | -al | |
| Ketone | Oxo- | -one | |
| Nitrile | Cyano- | -nitrile | |
| Ethers | (small)oxy- | _ | |
| Ester | Alkyl(OR')- | + | -oate(R+1) |
| Acyl halide | Halo carbonyl- | -oyl halide | |
| Amides | Carbamyl- | -amide(N-group1,group2) | |
| Anhydride | _ | -oic anhydride(Roic R'oic) | |
| Acid hydrazide{-CO-NHNH2} | _ | -ohydrazide | |
| Acid azide{-CO-N3} | _ | -azide | |
| Hydroxamic acids{-CO-NHOH} | _ | -ohydroxamic | |
| Thioacids | Carbothioic acid- | -thioic acid | |
| Thioester | Alkyl(SR')- | + | -thioate (R+1) |
| Thiol | mercapto- | -thiol | |
| Thioether | Smallylthio- | _ [or Ryl R'yl thio ether] | |
| Amines(1°) | Amino- | -amine | |
| Amines(2°&3°) | N-smallyl | + | -amine |
| Nitro{-NO2} | Nitro | _ | |
| Alkyl nitrite{-ONO} | _ | -nitrite | |
| Isonitrile | [Ryl isocyanide or (R+1)yl isonitrile or Ryl carbyl amine] | ||
| Sulphonic acids{-SO3H} | Sulpho- | -sulphonic acid | |
| Imines | Alakanal- | + | -imine |
| Cyclic ethers(Ring has n atoms) | 1,n-1-epoxy- | _ |
Special:
Lactones(cyclic esters)(n-member ring) (n-2)th greek letter-lactone
Lactam(cyclic amides)(n-member ring) (n-2)th greek letter-lactam
Cyclic compound nomenclature:
AlicyclicAliphatic compounds that have 1 ring
Cyclo-
BicyclicAliphatic compounds containing 2 rings and carbons common to both rings
bicyclo[mNumber of carbon atoms in the larger ring - 2,nNumber of carbon atoms in the smaller ring - 2,oNumber of carbon atoms between the bridgeheads] (m+n+o+2)ane
Numbering from large ring to small ring
TricyclicAliphatic compounds containing 3 rings and 2 carbons common to the rings
tricyclo[mNumber of carbon atoms in largest ring - 2,nNumber of carbon atoms in the 2nd largest ring - 2,oNumber of carbon atoms in the smallest ring - 2,pNumber of carbon atoms between the bridgeheads] (m+n+o+p+2)ane
Numbering from large ring to small ring
SpiroAliphatic compounds containing 2 or more rings and having 1 carbon common between rings
spiro[mNumber of carbons in the smaller ring - 1,nNumber of carbons in the larger ring - 1] (m+n+1)ane
Numbering from small ring to large ring
Special rule:
When 3 or more like functional groups are present in an unbranched carbon chain then, their carbons are not part of the name of the chain
Ex: HOOC-CH2-CH2-CH(COOH)-CH2-CH2-COOH is named Penta-1,3,5-trioic acid
Functional group priority order:
-COOH > -SO3H > -COOR > -COX > -CONH2 > -C≡N > -CHO > -CO- > -OH > -NH2 > --C=C-- > -C≡C-
Aromatic named substituents:
| Substituent | Name |
|---|---|
| Ph- | Phenyl |
| Ph-CH2- | Benzyl |
| Ph-CH-- | Benzal |
| Ph-C--- | Benzo |
| Ph-CO- | Benzoyl |
| C6H4-- | o/m/p - phenylene |
| Ph-C≡N | Benzonitrile |
| Ph-OH | Phenol |
| Ph-CH3 | Toulene |
| Ph-COOH | Benzanoic acid |
| Ph-CHO | Benzaldehyde |
| Ph-CO-CH3 | Acetophenone |
| Ph-CO-Ph | Benzophenone |
| Ph-CH=CH2 | Styrene |
| Ph-O-CH3 | Anisole |
| Ph-NH2 | Aniline |
| Ph-SO3H | Benzene sulphonic acid |
| Me-Toulene | o/m/p - xylene |
| 1,3,5 trimethyl benzene | Mesitylene |
| Isopropyl benzene | Cumene |
| Ph-O-CH2-CH3 | Phenetole |
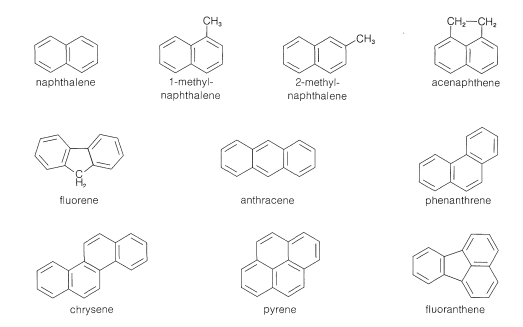
Multi-ringed aromatic compounds: