Heredity:
Passing genetic traits from parent to offspring
Classic genetics(oversimplified):
Gene is a section of DNA on a specific chromosomes
Polygenic trait are traits expressed due to many genes
Pleiotropic genes are genes that decide how multiple traits are expressed
Mendelian traits are traits represented by a single gene
An allele is a specific version of a gene
All cells in a body aside from gametes or undifferentiated stem cells are called somatic cells
All somatic cells are diploid
Gametes are haploid
Offspring inherit 2 alleles, one from each parent
In mendelian traits, alleles are either dominant or recessive.
Dominant alleles represent their phenotype in both heterozygous and homozygous conditions{2 different/ 2 same alleles}
Recessive traits are only expressed in homozygous conditions
Traits inherited from sex chromosomes can be passed down with just 1 copy of an allele as the y chromosome is smaller and missing some genes.
This makes recessive traits(like balding) more common in men.
It also contains genes for making ear hair that are not present on the x chromosome
Nucleic acids:
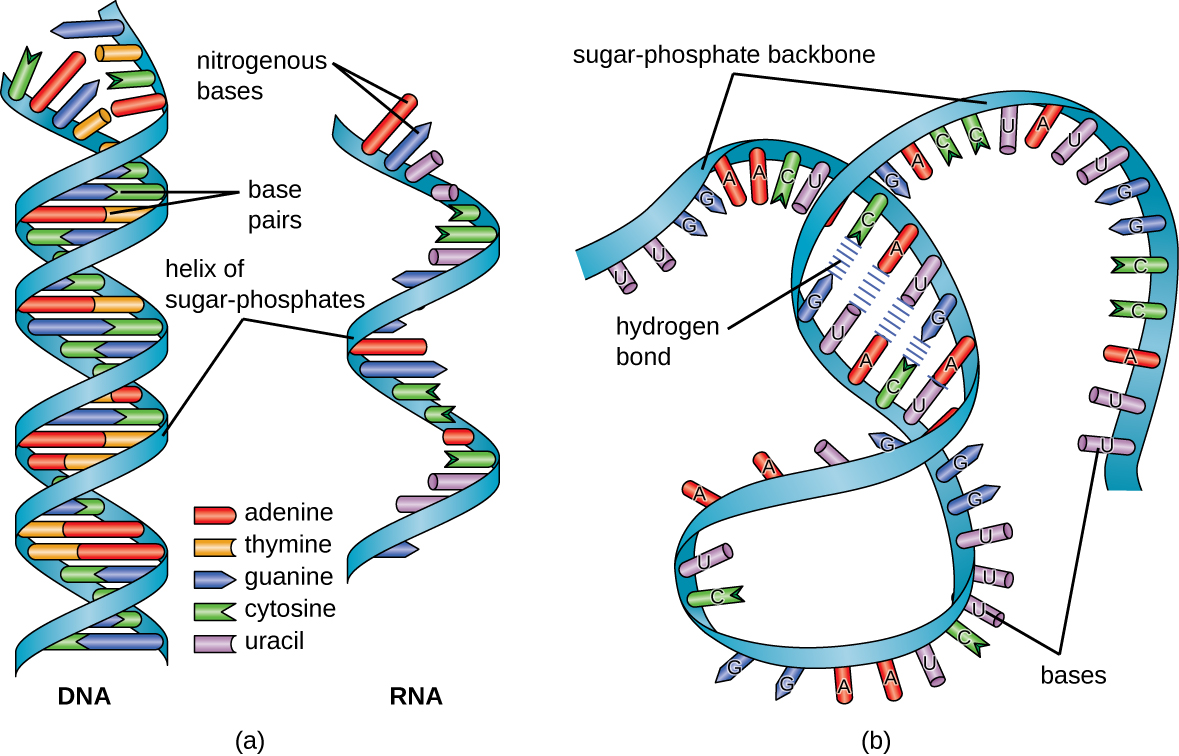
Polymers of nucleotides are polynucleotides
Each nucleotide contains deoxyribose(DNA)/ribose(RNA) bonded to a phosphate group and either cytosine , guanine , Adenine , thymine(DNA)/uracil(RNA)
The carbon attached to the nitrogenous base is labelled 1 prime and the rest are labelled by increasing numbers in a clockwise manner.
DNA:
Stores genetic information(cell activity things)
Pair of polynucleotides held tightly together by hydrogen bonds in double helix
In DNA, the phosphate group is bonded to both the 5 prime and 3 prime carbons
The 2 molecules of DNA are antiparallel to each other
One strand is upside down compared to the other one has a phosphate group at the "top" and the other has a hydroxyl(OH) group.
The direction with phosphate at the top and hydroxyl group at the bottom is called the 5' 3' direction, the other direction is called the 3' 5' direction
Adenine(A) can only form hydrogen bond(H-bond) with Thymine(T) and cytosine (C) can only make H-bond with guanine(G)
{A forms pair with uracil(U) in case of RNA}
The GC pair is slightly stronger than the AT pair (3 H-bond compared to 2)
Cells need to replicate DNA while splitting
RNA:
Similar to DNA but only 1 strand , has ribose instead of deoxyribose and uracil instead of thymine




