Photosynthesis:
It requires water carbon dioxide and sunlight
Water comes through the xylem, carbon dioxide through the stoma and sunlight through chlorophyll
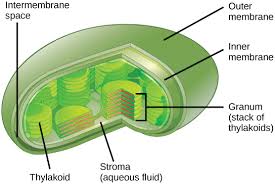
Chlorophyll is in membranous sacks called thylakoids, they are stacked into grana
Inside thylakoid is lumen and outside the thylakoid(inside chloroplast) is stroma
Thylakoid membrane is made of phospholipid bilayers
Light dependent reactions:
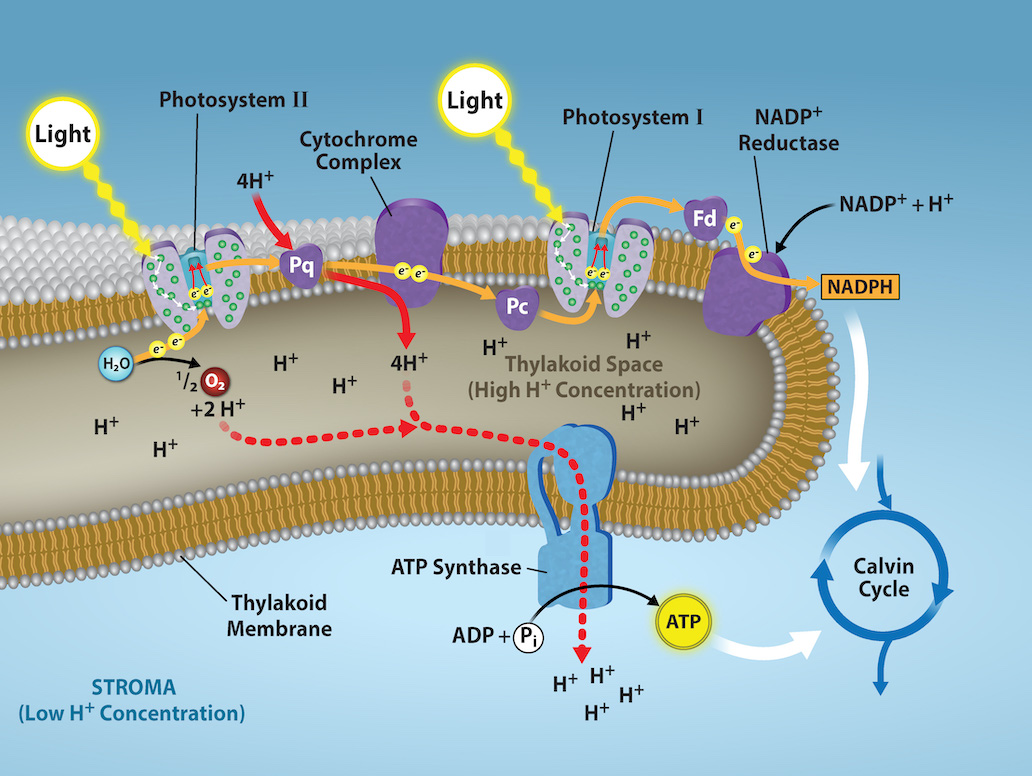
When a photon from the sun hits the chlorophyll, an electron gets excited, when 2 electrons are excited then photosynthesis starts
This chlorophyll is part of a complex called photo system 2 or PS2 containing at least 99 different chemicals (including 30 chlorophyll molecules)
It is one of 4 protein complexes involved in light dependent reactions
These protein complexes straddle the thylakoid membrane.
The excited electrons are transported by a special protein called a mobile electron carrier.
The chlorophyll and the rest of PS2 splits a water molecule into hydrogen and oxygen using some energy from one of the electrons.
This then takes one electron from the hydrogen to make a proton.
This electron along with the other is then transported to the second protein complex, cytochrome complex
The cytochrome complex is an intermediary between PS2 and PS1 and takes some energy from the electron to pump a proton into the thylakoid.
The proton from this and splitting the water is used to create ATP by being pumped into the ATP synthase
The electron is then delivered to PS1 which is similar to PS2.
Photons then excite electrons at PS1 and the electrons are transported to NADP+ reductase which helps combine 2 electrons , 1 proton and NADP+ into NADPH
The result is formation of NADPH, ATP and oxygen
Light independent reactions:
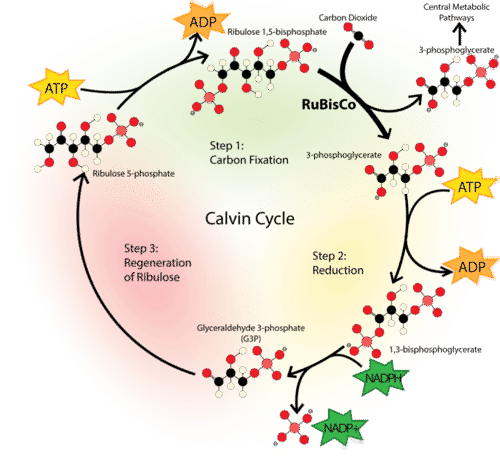
Also called calvin cycle
The first step is carbon fixation where a CO_2 molecule is fixed onto 5 carbon Ribulose Bisphosphate(RuBP) present in the chloroplast.
This is done with the help of an enzyme called RuBisCo(half the time it adds O_2 instead making a toxic byproduct)
The new 6 carbon molecule is unstable and splits into 2 molecules of 3-Phosphoglycerate.
Step 2 is reduction, some ATP adds a phosphate group onto 3-Phosphoglycerate
NADPH removes one phosphate group and adds some electron onto it turning into Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)
G3P is high energy 3 carbon compound that can be converted into many carbohydrates like glucose,cellulose or starch
5 G3P s are required to regenerate the RuBP so, 9 ATP , 6 NADPH are used to generate 6 G3P s of which 5 are reused to make 3 RuBP resulting in 1 G3P




