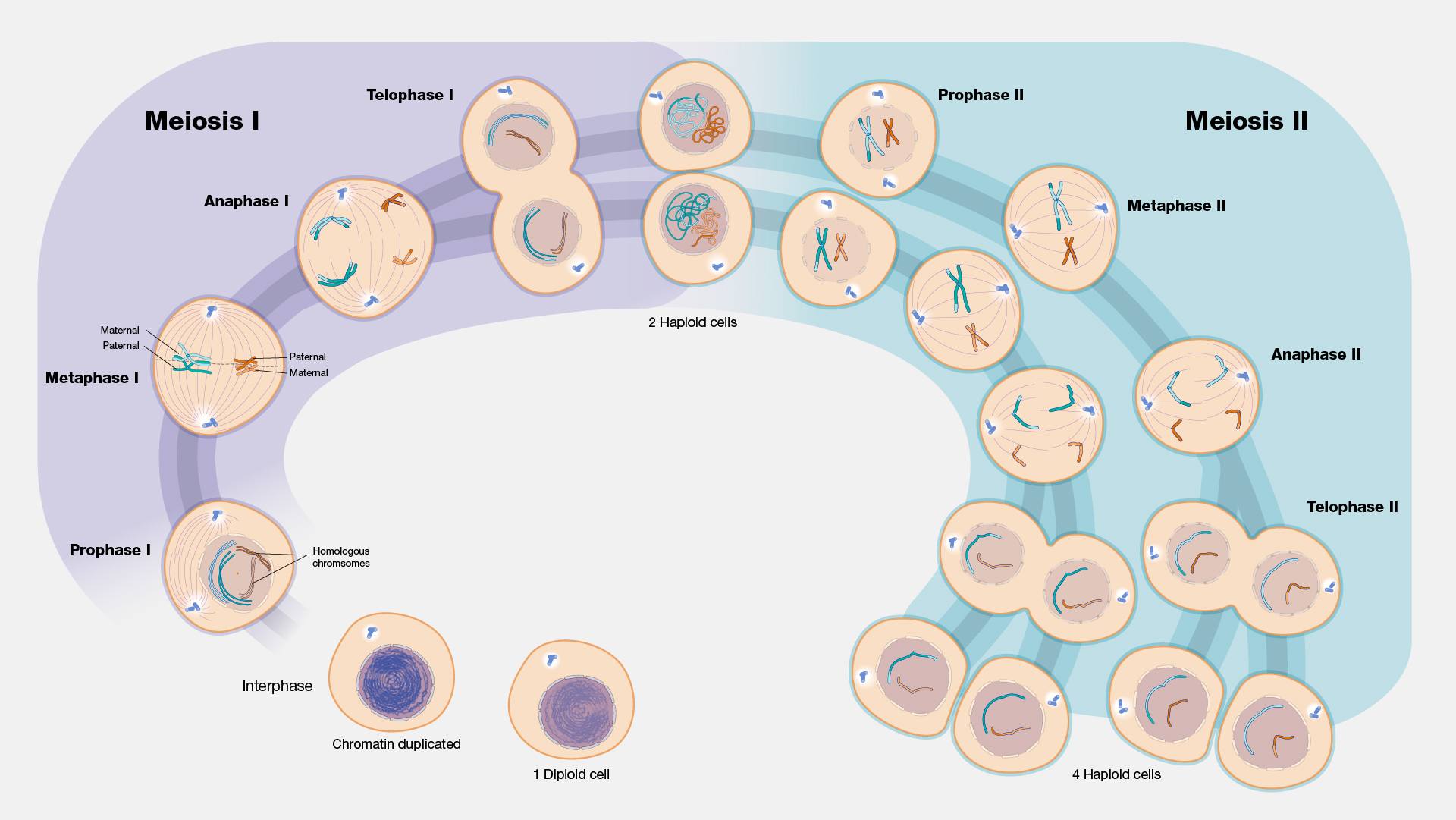
Meiosis:
Courtesy:National Human Genome Research Institute
Homologous chromosome pairs:
In the 22 pairs of autosomes, each pair has 2 chromosomes, one inherited from the father and the other from the mother.
These are similar to each other, alleles for the same trait in the same location but they are not identical, one may have different alleles etc.
Interphase:
Centrosome divides, DNA replicates, nuclear membrane disappears
Prophase 1:
Chromatin into chromosomes and double chromosome formed
Crossover:
Each of the homologues of the chromatids line up next to each other (mother's next to father's)
They then get tangled up with the chromatid of the other double chromosome.
The sex chromosomes do not go through cross over or recombination in men, they do in women(cuz XY are different and XX are same)
Recombination:
During cross over, they trade sections of DNA {from the same location} so they get the alleles of the same trait from the other homologues and vice-versa.
This creates new gene combinations on a single chromosome leading to variation. This lead to every egg/sperm cell having different genetic information
Metaphase 1:
Each chromosome lines up next to its homologous pair
Anaphase 1:
The homologous pairs get pulled apart and migrate to either end of the cell
Telophase 1:
The nuclear membrane reforms and the nucleolus also forms along with it.
The double-chromosomes relax back into chromatin
A crease forms between the cells and they move apart from each other, forming 2 non-identical haploid daughter cells(23 double chromosomes).
Prophase 2:
Centrosome duplicates , chromatin form into double chromosomes, nuclear membrane disappears, microtubules appear
Metaphase 2:
Double chromosomes are aligned at the centre of the cell in upright position
Anaphase 2:
Chromatids are pulled apart into separate chromosomes
Telophase 2:
Chromosomes uncoil into chromatin, nuclear membrane reforms, nucleolus form with it
Crease form between the cells and they move apart into non-identical daughter cells, in total forming 4 different non-identical daughter cells
For sperm, all 4 cells are the same size
For eggs, in telophase 1 more cytoplasm, organelles head into 1 cell and in telophase 2 the same thing happens in the bigger cell.
This results in 3 smaller cells and 1 larger cell. The large cell is the egg, the smaller cells are the polar bodies.
In humans, the polar bodies are useless and in plants, they get fertilised into the endosperm, food for the embryo.




