Mitosis:
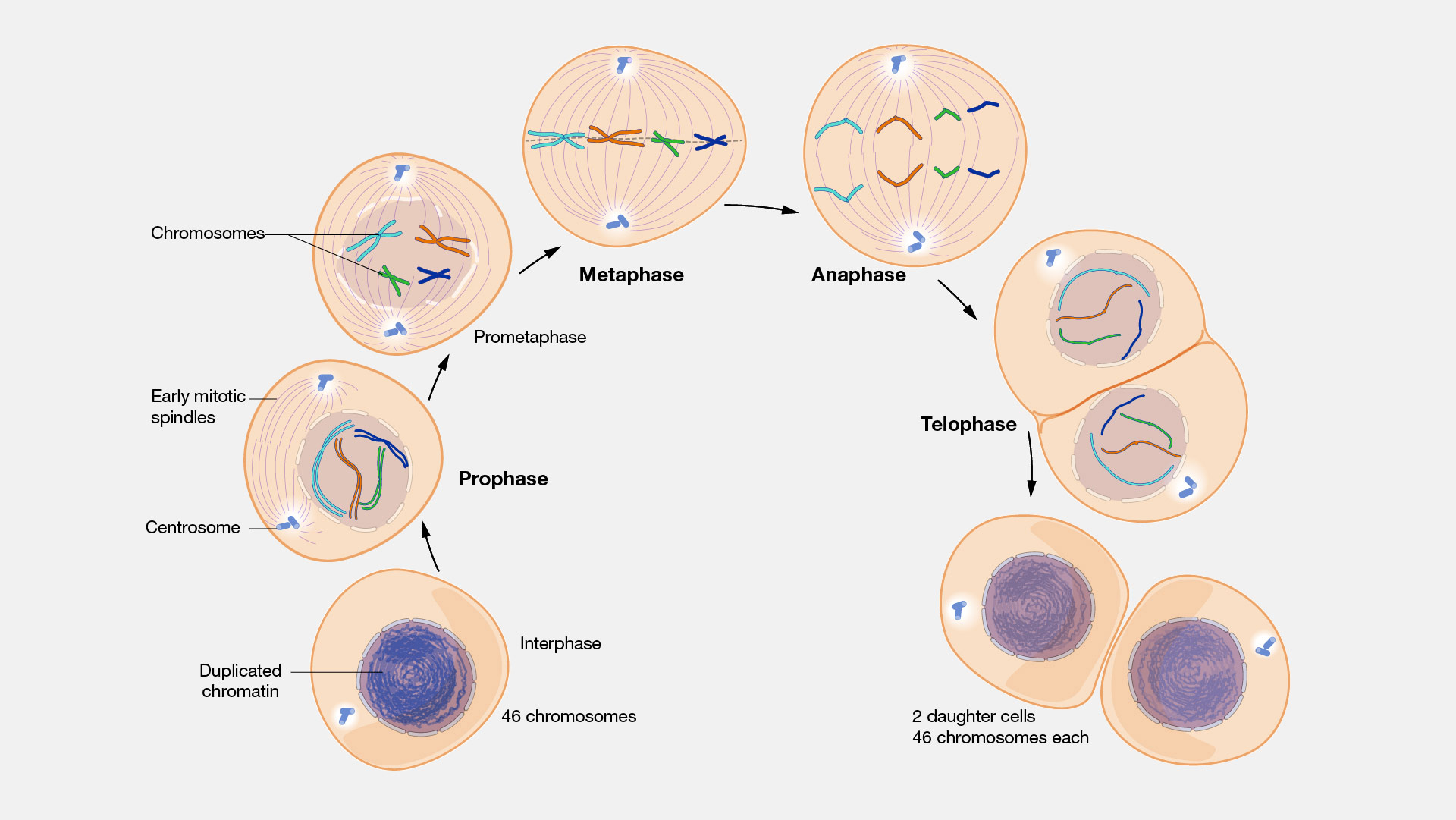
One eukaryotic cell splits into 2 daughter cells.
Courtesy:National Human Genome Research Institute
Interphase:
Most of the time of a cell is spent here, it is between episodes of mitosis
DNA is loosely coiled and messy , this mess is called chromatin.
The centrosome next to the nucleus duplicates itself.
The DNA replicates itself and now the cell has 2 copies of every strand
Prophase:
Chromatin wraps around itself and produces thick strands of DNA wrapped around proteins forming chromosomes
The nuclear membrane disappears
The duplicated chromosomes and are attached to the original chromosomes in a x-like shaped
Each of the chromosomes in the double chromosome is called a chromatid, the chromatids are linked in the middle by something called a centromere.
The centrosomes go to the opposite ends of the cell and they leave behind microtubules that connect the centrosomes
Metaphase:
Longest phase (up to 20mins)
Chromosomes attach themselves to the microtubules at the centromeres and start to move around by motor proteins(2 on each side of the centromere).
These motor proteins along with the help of another motor protein called dynein align the chromosome in the centre of the cell in the upright position
Anaphase:
The motor proteins pull hard and the chromatids separate and split into individual chromosomes and go the centrosomes at the ends of the cell
Telophase:
The nuclear membrane reforms and the nucleolus also forms along with it.
The chromosomes relax back into chromatin
A crease forms between the cells and they move apart from each other forming 2 identical daughter cells.




