Respiration:
Glucose + 6 Oxygen molecules gives 6 CO_2 + 6 water molecules and energy
This energy needs to be turned into ATP to be used by our bodies
ATP is made of adenine bonded to ribose bonded to a chain of 3 phosphate molecules
It can release energy by removing one of the phosphate groups, replacing it with OH , forming ADP {Hydrolysis}
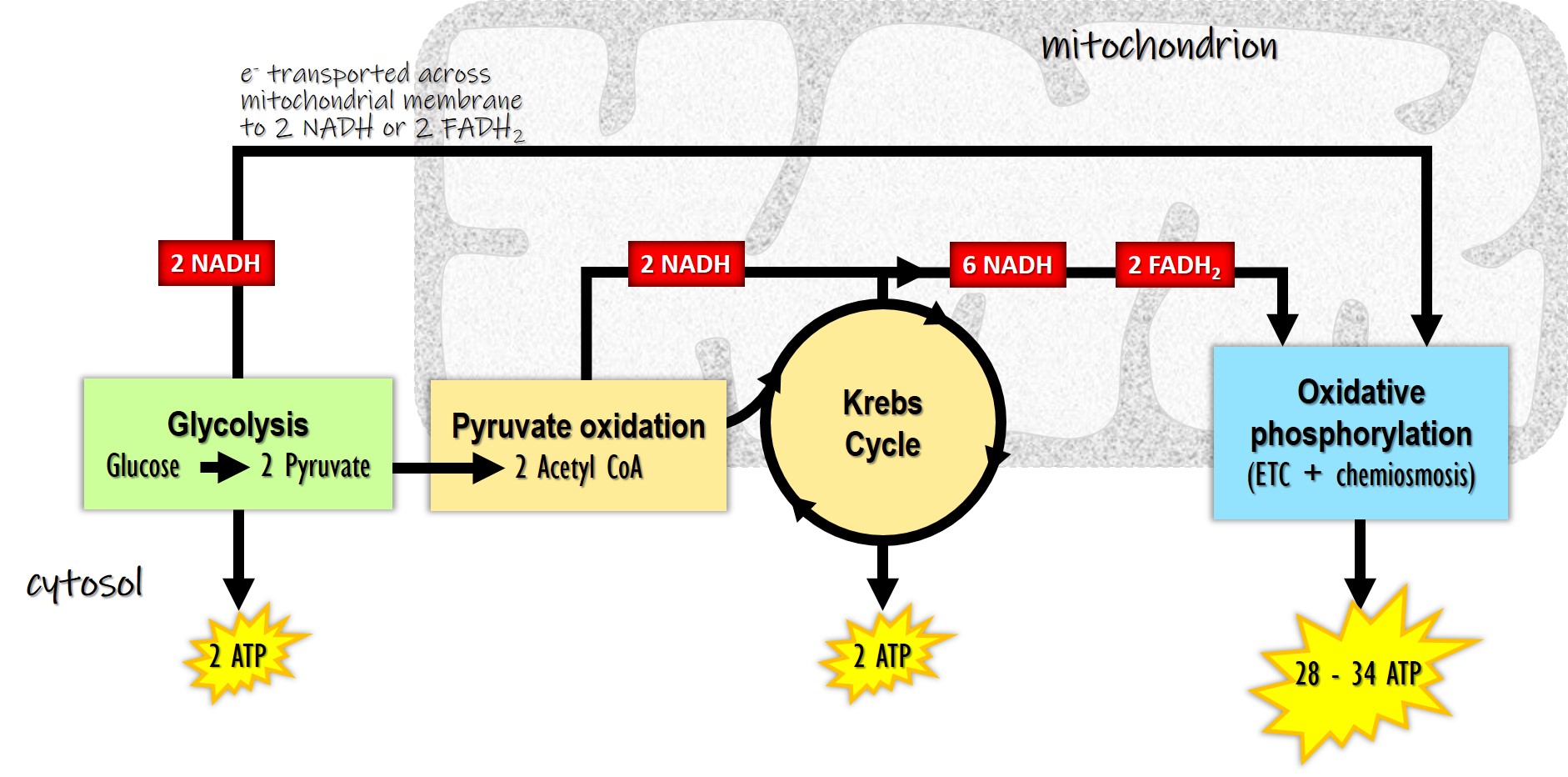
ATP is made from glucose over 3 steps:
Glycolysis:
Glucose contains 6 carbons and is broken into 2 molecules containing 3 carbons called Pyruvic acid/Pyruvate molecule.
Uses 2 ATP and generates 4 ATP{2 extra}.
In total, it ends up generating 4 ATP , 2 pyruvates and 2 NADH{stores energy, used to create ATP}
It is an anaerobic process, pyruvate in the absence of oxygen undergoes fermentation
Fermentation generates some NAD+ to help maintain glycolysis in absence of oxygen
This results in byproducts like lactic acid in humans and ethyl alcohol in yeast
Krebs cycle:
Inside inner mitochondrial membrane.
Takes Pyruvates and turns 2 ADP into 2 ATP per glucose molecule and energy
Pyruvate is oxidised into carbon dioxide and acetyl coenzyme A(Acetyl coA)
2 NADH is formed in this per glucose molecule.
Acetyl coA is joined with a 4 carbon molecule(oxaloacetic acid) to make
Citric acid, citric acid is oxidised again over a few steps to make oxaloacetic acid
NAD+ , FAD are enzymes related to B vitamins.They pickup energised electrons and hydrogens from pyruvate turning them into NADH and FADH_2.
Each Acetyl coA gives 3 NADH and 1 FADH_2
Electron transport chain:
The energy from the electrons from NADH and FADH_2 will pump along a chain of channel proteins across the inner membrane of the mitochondria.
These proteins will swap electrons to send hydrogen protons from inside the mitochondria to its outer compartment
They will then try to enter the inner compartment through the ATP synthase, where their energy is used to make 34 ATP.
Each NADH makes 3 ATP and FADH_2 makes 2 ATP each




